Irritable bowel syndrome
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
|
This article is in need of attention from an expert on the subject. Please help recruit one or improve this article yourself. See the talk page for details. Please consider using {{Expert-subject}} to associate this request with a WikiProject. (January 2009) |
|
Irritable bowel syndrome synonymous with GILL/HT/IB |
|
|
Classification and external resources |
|
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a blanket term for a variety of diseases causing discomfort in the gastro-intestinal tract. Also called spastic colon, it is a functional bowel disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and alteration of bowel habits in the absence of any organic cause. In some cases, the symptoms are relieved by bowel movements.[1] Diarrhea or constipation may predominate, or they may alternate (classified as IBS-D, IBS-C or IBS-A, respectively). IBS may begin after an infection (post-infectious, IBS-PI) or a stressful life event or may begin at onset of maturity without any other medical indicators.
Although there is no cure for IBS, there are treatments which attempt to relieve symptoms, including dietary adjustments, medication and psychological interventions. Patient education and a good doctor-patient relationship are also important.[1]
Several conditions may present as IBS including celiac disease, mild infections, parasitic infections like giardiasis[2], several inflammatory bowel diseases, functional chronic constipation, and chronic functional abdominal pain. In IBS, routine clinical tests yield no abnormalities, though the bowels may be more sensitive to certain stimuli, such as balloon insufflation testing. The exact cause of IBS is unknown. The most common theory is that IBS is a disorder of the interaction between the brain and the gastrointestinal tract, although there may also be abnormalities in the gut flora or the immune system.[3][4]
IBS does not lead to more serious conditions in most patients.[5][6][7][8][9] But it is a source of chronic pain, fatigue and other symptoms, and it increases a patient's medical costs,[10][11] and contributes to work absenteeism.[12][13] Researchers have reported that the high prevalence of IBS,[14][15][16] in conjunction with increased costs produces a disease with a high societal cost.[17] It is also regarded as a chronic illness and can dramatically affect the quality of a sufferer's life.
[edit] Classification
IBS can be classified as either diarrhea-predominant (IBS-D), constipation-predominant (IBS-C) or IBS with alternating stool pattern (IBS-A or pain-predominant[18]). In some individuals, IBS may have an acute onset and develop after an infectious illness characterized by two or more of the following: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, or positive stool culture. This post-infective syndrome has consequently been termed "post-infectious IBS" (IBS-PI).
[edit] Symptoms
The primary symptoms of IBS are abdominal pain or discomfort in association with frequent diarrhea or constipation, a change in bowel habits.[19] There may also be urgency for bowel movements, a feeling of incomplete evacuation (tenesmus), bloating or abdominal distention.[20] People with IBS more commonly than others have gastroesophageal reflux, symptoms relating to the genitourinary system, psychological symptoms, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, headache and backache.[20][21]
A person with irritable bowel syndrome could also experience lethargy, first depression and disturbance when sleeping. Digestive disorder can develop at any age, but usually first experienced between ages 15 and 40.[22]
[edit] Diagnosis
There is no specific laboratory or imaging test which can be performed to diagnose irritable bowel syndrome.[23] Diagnosis of IBS involves excluding conditions which produce IBS-like symptoms, and then following a procedure to categorize the patient's symptoms.
[edit] Differential diagnosis
Because there are many causes of diarrhea that give IBS-like symptoms, the American Gastroenterological Association has published a set of guidelines for tests to be performed to rule out other causes for these symptoms. These include gastrointestinal infections, lactose intolerance and Coeliac disease. Research has suggested that these guidelines are not always followed.[23] Once other causes have been excluded, the diagnosis of IBS is performed using a diagnostic algorithm. Well-known algorithms include the Manning Criteria, the obsolete Rome I and II criteria, the Kruis Criteria, and studies have compared their reliability.[24] The more recent Rome III Process was published in 2006. Physicians may choose to use one of these guidelines, or may simply choose to rely on their own anecdotal experience with past patients. The algorithm may include additional tests to guard against mis-diagnosis of other diseases as IBS. Such "red flag" symptoms may include weight loss, GI bleeding, anemia, or nocturnal symptoms. However, researchers have noted that red flag conditions may not always contribute to accuracy in diagnosis for instance, as many as 31% of IBS patients have blood in their stool.[24]
The diagnostic algorithm identifies a name which can be applied to the patient's condition based on the combination of the patient's symptoms of diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation. For example, the statement "50% of returning travelers had developed functional diarrhea while 25% had developed IBS" would mean that half the travelers had diarrhea while a quarter had diarrhea with abdominal pain. While some researchers believe this categorization system will help physicians understand IBS, others have questioned the value of the system and suggested that all IBS patients have the same underlying disease but with different symptoms.[25]
[edit] Misdiagnosis
Published research has demonstrated that some poor patient outcomes are due to treatable causes of diarrhea being mis-diagnosed as IBS. Common examples include infectious diseases, celiac disease,[26] helicobacter pylori,[27][28] parasites.[4][29][30] See List of causes of diarrhea for other conditions which can cause diarrhea.
Celiac disease in particular is often misdiagnosed as IBS. The American College of Gastroenterology recommends that all patients with symptoms of IBS be tested for celiac disease.[31] Chronic use of certain sedative-hypnotic drugs especially the benzodiazepines may cause irritable bowel like symptoms which can lead to a misdiagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome.[32]
[edit] Medical conditions that accompany IBS
Researchers have identified several medical conditions, or comorbidities, which appear with greater frequency in patients diagnosed with IBS.
Headache, Fibromyalgia, Chronic fatigue syndrome and Depression: A study of 97,593 individuals with IBS identified comorbidities as headache, fibromyalgia, and depression.[33] A systematic review found that IBS occurs in 51% of chronic fatigue syndrome patients and 49% of fibromyalgia patients, and psychiatric disorders were found to occur in 94% of IBS patients.[21]
Inflammatory bowel disease: Some researchers have suggested that IBS is a type of low-grade inflammatory bowel disease.[5] Researchers have suggested that IBS and IBD are interrelated diseases,[6] noting that patients with IBD experience IBS-like symptoms when their IBD is in remission.[7][8] A 3-year study found that patients diagnosed with IBS were 16.3 times more likely to develop IBD during the study period.[9] Serum markers associated with inflammation have also been found in patients with IBS (see Causes).
Abdominal surgery: A recent (2008) study found that IBS patients are at increased risk of having unnecessary cholecystectomy (gall bladder removal surgery) not due to an increased risk of gallstones, but rather to abdominal pain, awareness of having gallstones, and inappropriate surgical indications.[34] A 2005 study published in Digestive Disease Science reported that IBS patients are 87% more likely to undergo abdominal and pelvic surgery, and three times more likely to undergo gallbladder surgery.[35] A study published in Gastroenterology came to similar conclusions, and also noted IBS patients were twice as likely to undergo hysterectomy.[36]
Endometriosis: One study has reported a statistically significant link between migraine headaches, IBS, and endometriosis.[37]
Other chronic disorders: Interstitial cystitis may be associated with other chronic pain syndromes, such as irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia. The connection between these syndromes is unknown.[38]
[edit] Etiology
The cause of IBS is not known, but several hypotheses have been proposed. The risk of developing IBS increases sixfold after acute gastrointestinal infection. Post-infection, further risk factors are young age, prolonged fever, anxiety and depression.[39]
[edit] Psychosomatic illness
Publications suggesting the role of brain-gut "axis" appeared in the 1990s, such as a study entitled Brain-gut response to stress and cholinergic stimulation in IBS published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology in 1993.[40] A 1997 study published in Gut magazine suggested that IBS was associated with a "derailing of the brain-gut axis."[41] Psychological factors are still thought to be important in the etiology of IBS,[21] and the symptoms defining the condition are referred to by some doctors as medically unexplained symptoms,[42] a term some psychiatrists consider synonymous with somatoform disorder.
[edit] Immune reaction
|
This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2009) |
From the late 1990s, research publications began identifying specific biochemical changes present in tissue biopsies and serum samples from IBS patients. These studies identified cytokines and secretory products in tissues taken from IBS patients. The cytokines identified in IBS patients produce inflammation and are associated with the body's immune response.
[edit] Active infections
There is research to support IBS being caused by an as-yet undiscovered active infection. Most recently, a study has found that the antibiotic Rifaximin provides sustained relief for IBS patients.[43] While some researchers see this as evidence that IBS is related to an undiscovered agent, others believe IBS patients suffer from overgrowth of intestinal flora and the antibiotics are effective in reducing the overgrowth (known as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth).[44] Other researchers have focused on an unrecognized protozoal infection as a cause of IBS[4] as certain protozoal infections occur more frequently in IBS patients.[45][46] Two of the protozoa investigated have a high prevalence in industrialized countries and infect the bowel, but little is known about them as they are recently emerged pathogens.
Blastocystis is a single-celled organism which has been reported to produce symptoms of abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea in patients, along with headaches and depression,[47] though these reports are contested by some physicians.[48] Studies from research hospitals in various countries have identified high Blastocystis infection rates in IBS patients, with 38% being reported from London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine,[49] 47% reported from the Department of Gastroenterology at Aga Khan University in Pakistan[45] and 18.1% reported from the Institute of Diseases and Public Health at University of Ancona in Italy.[46] Reports from all three groups indicate a Blastocystis prevalence of approximately 7% in non-IBS patients. Researchers have noted that clinical diagnostics fail to identify infection,[50] and Blastocystis may not respond to treatment with common antiprotozoals.[51][52][53][54]
Prevalence of protozoal infections in industrialized countries (United States and Canada) in 21st century.[55][56]
Dientamoeba fragilis is a single-celled organism which produces abdominal pain and diarrhea. Studies have reported a high incidence of infection in developed countries, and symptoms of patients resolve following antibiotic treatment.[55][57] One study reported on a large group of patients with IBS-like symptoms who were found to be infected with Dientamoeba fragilis, and experienced resolution of symptoms following treatment.[58] Researchers have noted that methods used clinically may fail to detect some Dientamoeba fragilis infections.[57] It is also found in people without IBS. [59]
[edit] Treatment
A questionnaire in 2006 designed to identify patients perceptions about IBS, their preferences on the type of information they need, as well as educational media and expectations from health care providers, revealed misperceptions about IBS developing into other conditions, including colitis, malnutrition, and cancer.[60]
The survey found IBS patients were most interested in learning about foods to avoid (60%), causes of IBS (55%), medications (58%), coping strategies (56%), and psychological factors related to IBS (55%). The respondents indicated that they wanted their physicians to be available via phone or e-mail following a visit (80%), have the ability to listen (80%), and provide hope (73%) and support (63%).
[edit] Diet
Many different dietary modifications have been attempted to improve the symptoms of IBS. Some are effective in certain sub populations. As lactose intolerance and IBS have such similar symptoms a trial of a lactose free diet is often recommended.[61] Fiber supplements have not been found to be effective in the general IBS population.[62] They however might be beneficial in those who have a predominance of constipation.
Definitive determination of dietary issues can be accomplished by testing for the physiological effects of specific foods. The ELISA food allergy panel can identify specific foods to which a patient has a reaction. Other testing can determine if there are nutritional deficiencies secondary to diet that may also play a role. Removal of foods causing IgG immune response as measured using the ELISA food panel has been shown to substantially decrease symptoms of IBS in several studies.[63]
There is no evidence that digestion of food or absorption of nutrients is problematic for those with IBS at rates different from those without IBS. However, the very act of eating or drinking can provoke an overreaction of the gastrocolic response in some patients with IBS due to their heightened visceral sensitivity, and this can lead to abdominal pain, diarrhea, and/or constipation.[64]
Several of the most common dietary triggers are well-established by clinical studies at this point; research has shown that IBS patients are hypersensitive to fats and fructose.[65][66]
It also appears that some foods are more difficult for the gut as evidenced by elevated food-specific IgG4 antibodies being present,[67][68] while others increase colonic contractions, which may be painful, due to increased visceral sensitivity in IBS sufferers.[69]
Fiber
In patients who have constipation predominant irritable bowel, soluble fiber at doses of 20 grams per day can reduce overall symptoms but will not reduce pain. The research supporting dietary fiber contains conflicting, small studies that are complicated by the heterogeneity of types of fiber and doses used.[70] The one meta-analysis that controlled for solubility found that only soluble fiber improved global symptoms of irritable bowel and neither type of fiber reduced pain[70] Positive studies have used 20-30 grams per day of psyllium seed.[71][72] One study specifically examined the effect of dose and found that 20 grams of ispaghula husk was better than 10 grams and equivalent to 30 grams per day[73] An uncontrolled study noted increased symptoms with insoluble fibers.[74] It is unclear if these symptoms are truly increased compared to a control group. If the symptoms are increased, it is unclear if these patients were diarrhea predominant (which can be exacerbated by insoluble fiber[75][76]), or if the increase is temporary before benefit occurs.
[edit] Medication
Medications may consist of stool softeners and laxatives in constipation-predominant IBS, and antidiarrheals (e.g., opiate, opioid or opioid analogs such as loperamide, codeine, diphenoxylate) in diarrhea-predominant IBS for mild symptoms.[77][78][79]
Drugs affecting serotonin (5-HT) in the intestines can help reduce symptoms.[80] Serotonin stimulates the gut motility and so agonists can help constipation-predominate irritable bowel, while antagonists can help diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel.
[edit] Laxatives
Main article: Laxative
For patients who do not adequately respond to dietary fiber, osmotic agents such as polyethylene glycol, sorbitol, and lactulose can help avoid 'cathartic colon' which has been associated with stimulant laxatives.[81] Among the osmotic laxatives, 17 to 26 grams/day of polyethylene glycol (PEG) has been well studied.
- Lubiprostone (Amitiza), is a gastrointestinal agent used for the treatment of idiopathic chronic constipation and constipation-predominant IBS. It is well-tolerated in adults, including elderly patients. As of July 20, 2006, Lubiprostone had not been studied in pediatric patients. Lubiprostone is a bicyclic fatty acid (prostaglandin E1 derivative) which acts by specifically activating ClC-2 chloride channels on the apical aspect of gastrointestinal epithelial cells, producing a chloride-rich fluid secretion. These secretions soften the stool, increase motility, and promote spontaneous bowel movements (SBM). Unlike many laxative products, Lubiprostone does not show signs of tolerance, dependency, or altered serum electrolyte concentration.
[edit] Antispasmodics
Main article: Antispasmodic
The use of antispasmodic drugs (e.g. anticholinergics such as hyoscyamine or dicyclomine) may help patients, especially those with cramps or diarrhea. A meta-analysis by the Cochrane Collaboration concludes that if 6 patients are treated with antispasmodics, 1 patient will benefit.[77] Antispasmodics can be divided in two groups: neurotropics and musculotropics. Neurotropics, such as atropine, act at the nerve fibre of the parasympathicus but also affect other nerves and have side effects. Musculotropics such as mebeverine act directly at the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract, relieving spasm without affecting normal gut motility.[citation needed] Since this action is not mediated by the autonomic nervous system, the usual anticholinergic side effects are absent.[citation needed]
[edit] Serotonin agonists
- Tegaserod (Zelnorm), a selective 5-HT4 agonist for IBS-C, is available for relieving IBS constipation in women and chronic idiopathic constipation in men and women. On March 30, 2007, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requested that Novartis Pharmaceuticals voluntarily discontinue marketing of tegaserod based on the recently identified finding of an increased risk of serious cardiovascular adverse events (heart problems) associated with use of the drug. Novartis agreed to voluntarily suspend marketing of the drug in the United States and in many other countries. On July 27, 2007 the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a limited treatment IND program for tegaserod in the USA to allow restricted access to the medication for patients in need if no comparable alternative drug or therapy is available to treat the disease. The USA FDA had issued two previous warnings about the serious consequences of Tegaserod. In 2005, tegaserod was rejected as an IBS medication by the European Union. Tegaserod, marketed as Zelnorm in the United States, was the only agent approved to treat the multiple symptoms of IBS (in women only), including constipation, abdominal pain and bloating. A meta-analysis by the Cochrane Collaboration concludes that if 17 patients are treated with typical doses of tegaserod, 1 patient will benefit.[82]
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor anti-depressants (SSRIs), because of their serotonergic effect, would seem to help IBS, especially patients who are constipation predominant. Initial crossover studies[83] and randomized controlled trials[84][85][86] support this role.
[edit] Serotonin antagonists
- Alosetron, a selective 5-HT3 antagonist for IBS-D, which is only available for women in the United States under a restricted access program, due to severe risks of side-effects if taken mistakenly by IBS-A or IBS-C sufferers.[citation needed]
- Cilansetron, also a selective 5-HT3 antagonist, is undergoing further clinical studies in Europe for IBS-D sufferers. In 2005, Solvay Pharmaceuticals withdrew Cilansetron from the United States regulatory approval process after receiving a "not approvable" action letter from the FDA requesting additional clinical trials.[citation needed]
[edit] Other agents
There is conflicting evidence about the benefit of antidepressants in IBS. Some meta-analysis have found a benefit while others have not.[87] A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of mainly TCAs found 3 patients have to be treated with TCAs for one patient to improve.[88] A separate randomized controlled trial found that TCAs are best for patients with diarrhea-predominant IBS.[89]
Recent studies have suggested that rifaximin can be used as an effective treatment for abdominal bloating and flatulence,[43][90] giving more credibility to the potential role of bacterial overgrowth in some patients with IBS.[91]
The use of opioids is controversial due to the lack of evidence supporting their benefit and the potential risk of tolerance, physical dependence and addiction.[92]
[edit] Psychotherapy
There is a strong brain-gut component to IBS. Cognitive behavioral therapy has been found to improve symptoms in a number of studies.[93][94] Relaxation therapy has also been found to helpful.[95]
[edit] Alternative treatments
Probiotics
A 2008 review has found probiotics to be beneficial in the treatment of IBS.[96] Many different type have be found to be effective including: Lactobacillus plantarum[97] and Bifidobacteria infantis;[98] however, one review found that only Bifidobacteria infantis showed efficacy.[99]
Iberogast
The multi-herbal extract Iberogast was found to be significantly superior to placebo via both an abdominal pain scale and an IBS symptom score after four weeks of treatment.[100]
Peppermint oil
Enteric coated peppermint oil capsules has been advocated for IBS symptoms in adults and children;[101] however, results from trials have been inconsistent.[102][103]
Acupuncture
Many sufferers of IBS seek relief using acupuncture.[citation needed] A meta-analysis by the Cochrane Collaboration however concluded that most trials are of poor quality and that it is unknown whether acupuncture is more effective than placebo.[104]
[edit] Epidemiology
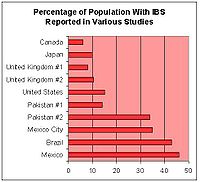
Percentage of population with IBS reported in various studies in different countries
By Country: Studies have reported that the prevalence of IBS varies by country and by age range examined. The bar graph at right shows the percentage of the population reporting symptoms of IBS in studies from various geographic regions (see table below for references).
The following table contains a list of studies performed in different countries that measured the prevalence of IBS and IBS-like symptoms:
|
[hide]Percentage of Population Reporting Symptoms of IBS in Various Studies from Various Geographic Areas ** Check the Rome criteria studies (eg, at PubMed) and see how the reported prevalence rates drop! Also, one should be wary of trusting many of these study results - ref. 'Havidol'. |
|||
|
Country |
Prevalence |
Author/Year |
Notes |
|
Canada |
6%[14] |
Boivin,2001 |
|
|
Japan |
10%[105] |
Quigley,2006 |
Study measured prevalence of GI abdominal pain/cramping |
|
United Kingdom |
8.2%[106] 10.5%[15] |
Ehlin,2003 Wilson,2004 |
Prevalence increased substantially 1970-2004 |
|
United States |
14.1%[107] |
Hungin, 2005 |
Most undiagnosed |
|
United States |
15%[14] |
Boivin,2001 |
Estimate |
|
Pakistan |
14%[108] |
Jafri, 2007 |
Much more common in 16-30 age range. Of IBS patients, 56% male, 44% female |
|
Pakistan |
34%[109] |
Jafri,2005 |
College students |
|
Mexico City |
35%[16] |
Schmulson, 2006 |
n=324. Also measured functional diarrhea and functional vomiting. High rates attributed to "stress of living in a populated city." |
|
Brazil |
43%[105] |
Quigley,2006 |
Study measured prevalence of GI abdominal pain/cramping |
|
Mexico |
46%[105] |
Quigley,2006 |
Study measured prevalence of GI abdominal pain/cramping |
Returning Travelers: A study of United States residents returning from international travel found a high rate of IBS and persistent diarrhea which developed during travel and persisted upon return. The study examined 83 subjects in Utah, most of whom were returning missionaries. Of the 68 who completed the gastrointestinal questionnaire, 27 reported persistent diarrhea that developed while traveling, and 10 reported persistent IBS that developed while traveling.[110]
[edit] Economic cost of IBS
The aggregate cost of irritable bowel syndrome in the United States has been estimated at $1.7-$10 billion in direct medical costs, with an additional $20 billion in indirect costs, for a total of $21.7-$30 billion.[17] A study by a managed care company comparing medical costs of IBS patients to non-IBS controls identified a 49% annual increase in medical costs associated with a diagnosis of IBS.[11] A 2007 study from a managed care oganization found that IBS patients incurred average annual direct costs of $5,049 and $406 in out-of-pocket expenses.[10] A study of workers with IBS found that they reported a 34.6% loss in productivity, corresponding to 13.8 hours lost per 40 hour week.[12] A study of employer-related health costs from a Fortune 100 company conducted with data from the 1990s found IBS patients incurred US $4527 in claims costs vs. $3276 for controls.[111] A study on Medicaid costs conducted in 2003 by the University of Georgia's College of Pharmacy and Novartis found IBS was associated in an increase of $962 in Medicaid costs in California, and $2191 in North Carolina. IBS patients had higher costs for physician visits, outpatients visits, and prescription drugs. The study suggested the costs associated with IBS were comparable to those found in asthma patients.[112]
[edit] Research spending on IBS
Further information: NIH funding of IBS Research
The National Institutes of Health provides a searchable database for grant awards since 1974 on its CRISP database, and provides dollar amounts for recent awards on its Intramural Grant Award Page. In 2006, the NIH awarded approximately 56 grants related to IBS, totalling approximately $18.7 million.
[edit] History
One of the first references to the concept of an "irritable bowel" appeared in the Rocky Mountain Medical Journal in 1950.[113] The term was used to categorize patients who developed symptoms of diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, but where no well-recognized infective cause could be found. Early theories suggested that the Irritable Bowel was caused by a psychosomatic, or mental disorder.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ a b Mayer EA (2008). "Clinical practice. Irritable bowel syndrome" ([dead link] Scholar search). N. Engl. J. Med. 358 (16): 16929. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0801447. PMID 18420501. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=18420501&promo=ONFLNS19.
- ^ Intestinal Infection
- ^ Yang CM, Li YQ (2007). "[The therapeutic effects of eliminating allergic foods according to food-specific IgG antibodies in irritable bowel syndrome]" (in Chinese). Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 46 (8): 6413. PMID 17967233.
- ^ a b c Stark D, van Hal S, Marriott D, Ellis J, Harkness J (2007). "Irritable bowel syndrome: a review on the role of intestinal protozoa and the importance of their detection and diagnosis". Int. J. Parasitol. 37 (1): 1120. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.09.009. PMID 17070814.
- ^ a b Bercik P, Verdu EF, Collins SM (2005). "Is irritable bowel syndrome a low-grade inflammatory bowel disease?". Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 34 (2): 23545, vi-vii. doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2005.02.007. PMID 15862932.
- ^ a b Quigley EM (2005). "Irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease: interrelated diseases?". Chinese journal of digestive diseases 6 (3): 12232. doi:10.1111/j.1443-9573.2005.00202.x. PMID 16045602.
- ^ a b Simr้n M, Axelsson J, Gillberg R, Abrahamsson H, Svedlund J, Bj๖rnsson ES (2002). "Quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease in remission: the impact of IBS-like symptoms and associated psychological factors". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 97 (2): 38996. PMID 11866278.
- ^ a b Minderhoud IM, Oldenburg B, Wismeijer JA, van Berge Henegouwen GP, Smout AJ (2004). "IBS-like symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in remission; relationships with quality of life and coping behavior". Dig. Dis. Sci. 49 (3): 46974. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000020506.84248.f9. PMID 15139501.
- ^ a b Garcํa Rodrํguez LA, Ruig๓mez A, Wallander MA, Johansson S, Olbe L (2000). "Detection of colorectal tumor and inflammatory bowel disease during follow-up of patients with initial diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 35 (3): 30611. doi:10.1080/003655200750024191. PMID 10766326.
- ^ a b Nyrop KA, Palsson OS, Levy RL, Korff MV, Feld AD, Turner MJ, Whitehead WE. (2007). "Costs of health care for irritable bowel syndrome, chronic constipation, functional diarrhoea and functional abdominal pain.". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26 (2): 23748. PMID 17593069.
- ^ a b Levy RL, Von Korff M, Whitehead WE, Stang P, Saunders K, Jhingran P, Barghout V, Feld AD. (2001). "Costs of care for irritable bowel syndrome patients in a health maintenance organization". Am J Gastroenterol 96 (11): 31229. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.05258.x. PMID 11721759.
- ^ a b Par้ P, Gray J, Lam S, et al. (2006). "Health-related quality of life, work productivity, and health care resource utilization of subjects with irritable bowel syndrome: baseline results from LOGIC (Longitudinal Outcomes Study of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Canada), a naturalistic study". Clinical therapeutics 28 (10): 172635; discussion 17101. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.10.010. PMID 17157129.
- ^ Maxion-Bergemann S, Thielecke F, Abel F, Bergemann R (2006). "Costs of irritable bowel syndrome in the UK and US". PharmacoEconomics 24 (1): 2137. doi:10.2165/00019053-200624010-00002. PMID 16445300.
- ^ a b c Boivin M. (2001 Oct;15). "Socioeconomic impact of irritable bowel syndrome in". Canada. Can J Gastroenterol. Suppl B: :8B11B.. PMID 11694908.
- ^ a b Wilson S, Roberts L, Roalfe A, Bridge P, Singh S. (2004). "Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome: a community survey.". Br J Gen Pract. 54 (504): 495502.. PMID 15239910.
- ^ a b Schmulson M, Ortiz O, Santiago-Lomeli M, Gutierrez-Reyes G, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC, Robles-Diaz G, Morgan D. (2006). "Frequency of functional bowel disorders among healthy volunteers in Mexico City." (PDF). Dig Dis. 24: 342. doi:10.1159/000092887. PMID 16849861. http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=92887&Ausgabe=231847&ProduktNr=224231&filename=92887.pdf.
- ^ a b Hulisz D. (2004). "The burden of illness of irritable bowel syndrome: current challenges and hope for the future.". J Manag Care Pharm. 10 (4): 299309. PMID 15298528.
- ^ Holten KB, Wetherington A, Bankston L (2003). "Diagnosing the patient with abdominal pain and altered bowel habits: is it irritable bowel syndrome?". Am Fam Physician 67 (10): 215762. PMID 12776965. http://www.aafp.org/afp/20030515/2157.html.
- ^ Schmulson MW, Chang L (1999). "Diagnostic approach to the patient with irritable bowel syndrome". Am. J. Med. 107 (5A): 20S26S. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(99)00278-8. PMID 10588169.
- ^ a b Talley NJ (2006). "Irritable bowel syndrome". Intern Med J 36 (11): 7248. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2006.01217.x. PMID 17040359. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=1444-0903&date=2006&volume=36&issue=11&spage=724.
- ^ a b c Whitehead WE, Palsson O, Jones KR (2002). "Systematic review of the comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome with other disorders: what are the causes and implications?". Gastroenterology 122 (4): 1140-56. PMID 11910364.
- ^ A-Stomach-Pain.com (2009), Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms
- ^ a b Yawn BP, Lydick E, Locke GR, Wollan PC, Bertram SL, Kurland MJ (2001). "Do published guidelines for evaluation of irritable bowel syndrome reflect practice?". BMC gastroenterology 1: 11. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-1-11. PMID 11701092.
- ^ a b Fass R, Longstreth GF, Pimentel M, et al. (2001). "Evidence- and consensus-based practice guidelines for the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome". Arch. Intern. Med. 161 (17): 20818. doi:10.1001/archinte.161.17.2081. PMID 11570936.
- ^ Talley NJ (2006). "A unifying hypothesis for the functional gastrointestinal disorders: really multiple diseases or one irritable gut?". Reviews in gastroenterological disorders 6 (2): 728. PMID 16699476.
- ^ Spiegel BM, DeRosa VP, Gralnek IM, Wang V, Dulai GS (2004). "Testing for celiac sprue in irritable bowel syndrome with predominant diarrhea: a cost-effectiveness analysis". Gastroenterology 126 (7): 172132. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.012. PMID 15188167.
- ^ Su YC, Wang WM, Wang SY, et al. (August 2000). "The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and functional dyspepsia in patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 95 (8): 19005. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02252.x. PMID 10950033.
- ^ Gerards C, Leodolter A, Glasbrenner B, Malfertheiner P (2001). "H. pylori infection and visceral hypersensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Dig Dis 19 (2): 1703. doi:10.1159/000050673. PMID 11549828. http://content.karger.com/produktedb/produkte.asp?typ=fulltext&file=ddi19170.
- ^ Grazioli B, Matera G, Laratta C, et al. (March 2006). "Giardia lamblia infection in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia: a prospective study". World J. Gastroenterol. 12 (12): 19414. PMID 16610003. http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/12/1941.asp.
- ^ Vernia P, Ricciardi MR, Frandina C, Bilotta T, Frieri G (1995). "Lactose malabsorption and irritable bowel syndrome. Effect of a long-term lactose-free diet". The Italian journal of gastroenterology 27 (3): 11721. PMID 7548919.
- ^ "American Journal of Gastroenterology - Abstract of article: An Evidence-Based Position Statement on the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome". http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal/v104/n1s/abs/ajg2008122a.html.
- ^ Professor C Heather Ashton (1987). "Benzodiazepine Withdrawal: Outcome in 50 Patients". British Journal of Addiction 82: 655671. http://www.benzo.org.uk/ashbzoc.htm.
- ^ Cole JA, Rothman KJ, Cabral HJ, Zhang Y, Farraye FA (2006). "Migraine, fibromyalgia, and depression among people with IBS: a prevalence study". BMC gastroenterology 6: 26. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-6-26. PMID 17007634.
- ^ Corazziari et al. (2008). "Gallstones, cholecystectomy and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) MICOL population-based study.". Dig Liver Dis. 40: 944. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2008.02.013. PMID 18406218.
- ^ Cole JA, Yeaw JM, Cutone JA, et al. (2005). "The incidence of abdominal and pelvic surgery among patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Dig. Dis. Sci. 50 (12): 226875. doi:10.1007/s10620-005-3047-1. PMID 16416174.
- ^ Longstreth GF, Yao JF (2004). "Irritable bowel syndrome and surgery: a multivariable analysis". Gastroenterology 126 (7): 166573. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.02.020. PMID 15188159.
- ^ Tietjen GE, Bushnell CD, Herial NA, Utley C, White L, Hafeez F (2007). "Endometriosis is associated with prevalence of comorbid conditions in migraine". Headache 47 (7): 106978. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00784.x. PMID 17635599.
- ^ Interstitial cystitis (Mayo Clinic)
- ^ Thabane M, Kottachchi DT, Marshall JK (2007). "The incidence and prognosis of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome.". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26 (4): 53544. PMID 17661757.
- ^ Fukudo S, Nomura T, Muranaka M, Taguchi F (1993). "Brain-gut response to stress and cholinergic stimulation in irritable bowel syndrome. A preliminary study". J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 17 (2): 13341. doi:10.1097/00004836-199309000-00009. PMID 8031340.
- ^ Orr WC, Crowell MD, Lin B, Harnish MJ, Chen JD (1997). "Sleep and gastric function in irritable bowel syndrome: derailing the brain-gut axis". Gut 41 (3): 3903. PMID 9378397.
- ^ Deary, V; Chalder, T; Sharpe, M (Oct 2007). "The cognitive behavioural model of medically unexplained symptoms: a theoretical and empirical review". Clinical psychology review 27 (7): 78197. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2007.07.002. ISSN 0272-7358. PMID 17822818. edit
- ^ a b Pimentel M, Park S, Mirocha J, Kane SV, Kong Y (2006). "The effect of a nonabsorbed oral antibiotic (rifaximin) on the symptoms of the irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized trial". Ann. Intern. Med. 145 (8): 55763. PMID 17043337.
- ^ Posserud I, Stotzer PO, Bj๖rnsson ES, Abrahamsson H, Simr้n M (2007). "Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Gut 56 (6): 8028. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.108712. PMID 17148502.
- ^ a b Yakoob J, Jafri W, Jafri N, et al. (2004). "Irritable bowel syndrome: in search of an etiology: role of Blastocystis hominis". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 70 (4): 3835. PMID 15100450.
- ^ a b Giacometti A, Cirioni O, Fiorentini A, Fortuna M, Scalise G (1999). "Irritable bowel syndrome in patients with Blastocystis hominis infection". Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 18 (6): 4369. doi:10.1007/s100960050314. PMID 10442423.
- ^ Qadri SM, al-Okaili GA, al-Dayel F (1989). "Clinical significance of Blastocystis hominis". J. Clin. Microbiol. 27 (11): 24079. PMID 2808664.
- ^ Markell EK, Udkow MP (1986). "Blastocystis hominis: pathogen or fellow traveler?". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 35 (5): 10236. PMID 3766850.
- ^ Windsor J (2007). "B. hominis and D. fragilis: Neglected human protozoa". British Biomedical Scientist: 5247. http://www.ibms.org/index.cfm?method=publications.biomedical_scientist&subpage=contents_2007_July.
- ^ Stensvold R, Brillowska-Dabrowska A, Nielsen HV, Arendrup MC (2006). "Detection of Blastocystis hominis in unpreserved stool specimens by using polymerase chain reaction". J. Parasitol. 92 (5): 10817. doi:10.1645/GE-840R.1. PMID 17152954.
- ^ Yakoob J, Jafri W, Jafri N, Islam M, Asim Beg M (2004). "In vitro susceptibility of Blastocystis hominis isolated from patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 61 (2): 757. PMID 15250669.
- ^ Haresh K, Suresh K, Khairul Anus A, Saminathan S (1999). "Isolate resistance of Blastocystis hominis to metronidazole". Trop. Med. Int. Health 4 (4): 2747. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3156.1999.00398.x. PMID 10357863.
- ^ Markell EK, Udkow MP (1986). "Blastocystis hominis: pathogen or fellow traveler?". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 35 (5): 10236. PMID 3766850.
- ^ Ok UZ, Girginkardeşler N, Balcioğlu C, Ertan P, Pirildar T, Kilimcioğlu AA (1999). "Effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethaxazole in Blastocystis hominis infection". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 94 (11): 32457. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01529.x. PMID 10566723.
- ^ a b Lagac้-Wiens PR, VanCaeseele PG, Koschik C (2006). "Dientamoeba fragilis: an emerging role in intestinal disease". CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 175 (5): 4689. doi:10.1503/cmaj.060265. PMID 16940260.
- ^ Amin OM (2002). "Seasonal prevalence of intestinal parasites in the United States during 2000". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 66 (6): 799803. PMID 12224595.
- ^ a b Stensvold CR, Arendrup MC, M๘lbak K, Nielsen HV (2007). "The prevalence of Dientamoeba fragilis in patients with suspected enteroparasitic disease in a metropolitan area in Denmark". Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 13 (8): 83942. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01760.x. PMID 17610603.
- ^ Borody T, Warren E, Wettstein A, et al. (2002). "Eradication of Dientamoeba fragilis can resolve IBS-like symptoms.". J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17 (Suppl; pages=A103).
- ^ http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/full/72/5/501
- ^ Halpert AD, Thomas AC, Hu Y, Morris CB, Bangdiwala SI, Drossman DA (2006). "A survey on patient educational needs in irritable bowel syndrome and attitudes toward participation in clinical research". J Clin Gastroenterol 40 (1): 3743. doi:10.1097/01.mcg.0000190759.95862.08. PMID 16340632.
- ^ B๖hmer CJ, Tuynman HA (August 2001). "The effect of a lactose-restricted diet in patients with a positive lactose tolerance test, earlier diagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome: a 5-year follow-up study". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13 (8): 9414. doi:10.1097/00042737-200108000-00011. PMID 11507359. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0954-691X&volume=13&issue=8&spage=941.
- ^ Brandt LJ, Bjorkman D, Fennerty MB, et al. (November 2002). "Systematic review on the management of irritable bowel syndrome in North America". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 97 (11 Suppl): S726. doi:10.1016/S0002-9270(02)05657-5. PMID 12425586.
- ^ Atkinson W, Sheldon TA, Shaath N, Whorwell PJ (2004). "Food elimination based on IgG antibodies in irritable bowel syndrome: a randomised controlled trial". Gut 53 (10): 145964. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.037697. PMID 15361495. http://gut.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/53/10/1459.
- ^ Sj๖lund K, Ekman R, Lindgren S, Rehfeld J (1996). "Disturbed motilin and cholecystokinin release in the irritable bowel syndrome.". Scand J Gastroenterol 31 (11): 11104. doi:10.3109/00365529609036895. PMID 8938905.
- ^ Caldarella MP, Milano A, Laterza F, Sacco F, Balatsinou C, Lapenna D, Pierdomenico SD, Cuccurullo F, Neri M (2005). "Visceral sensitivity and symptoms in patients with constipation- or diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): effect of a low-fat intraduodenal infusion". Am J Gastroenterol 100 (2): 3839. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.40100.x. PMID 15667496.
- ^ Choi, Y. Fats, Fructose May Contribute to IBS Symptoms. ACG 68th Annual Scientific Meeting: Abstract 21, presented October 13, 2003; Abstract 547, presented October 14, 2003.
- ^ Zar S, Benson MJ, Kumar D (2005). "Food-specific serum IgG4 and IgE titers to common food antigens in irritable bowel syndrome". Am J Gastroenterol 100 (7): 15507. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41348.x. PMID 15984980.
- ^ Zar S, Mincher L, Benson MJ, Kumar D (2005). "Food-specific IgG4 antibody-guided exclusion diet improves symptoms and rectal compliance in irritable bowel syndrome". Scand J Gastroenterol 40 (7): 8007. doi:10.1080/00365520510015593. PMID 16109655.
- ^ Mayer EA, Berman S, Suyenobu B, Labus J, Mandelkern MA, Naliboff BD, Chang L (2005). "Differences in brain responses to visceral pain between patients with irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis". Pain 115 (3): 398409. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2005.03.023. PMID 15911167.
- ^ a b Bijkerk C, Muris J, Knottnerus J, Hoes A, de Wit N (2004). "Systematic review: the role of different types of fiber in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19 (3): 24551. doi:10.1111/j.0269-2813.2004.01862.x. PMID 14984370.
- ^ Prior A, Whorwell P (1987). "Double blind study of ispaghula in irritable bowel syndrome.". Gut 28 (11): 15103. doi:10.1136/gut.28.11.1510. PMID 3322956.
- ^ Jalihal A, Kurian G (1990). "Ispaghula therapy in irritable bowel syndrome: improvement in overall well-being is related to reduction in bowel dissatisfaction.". J Gastroenterol Hepatol 5 (5): 50713. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.1990.tb01432.x. PMID 2129822.
- ^ Kumar A, Kumar N, Vij J, Sarin S, Anand B (1987). "Optimum dosage of ispaghula husk in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: correlation of symptom relief with whole gut transit time and stool weight.". Gut 28 (2): 1505. doi:10.1136/gut.28.2.150. PMID 3030900.
- ^ Francis CY, Whorwell PJ (1994). "Bran and irritable bowel syndrome: time for reappraisal". Lancet 344 (8914): 3940. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(94)91055-3. PMID 7912305.
- ^ Cann P, Read N, Holdsworth C, Barends D (1984). "Role of loperamide and placebo in management of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).". Dig Dis Sci 29 (3): 23947. doi:10.1007/BF01296258. PMID 6365490.
- ^ Cann P, Read N, Holdsworth C (1984). "What is the benefit of coarse wheat bran in patients with irritable bowel syndrome?". Gut 25 (2): 16873. doi:10.1136/gut.25.2.168. PMID 6319244.
- ^ a b Quartero A, Meineche-Schmidt V, Muris J, Rubin G, de Wit N (2005). "Bulking agents, antispasmodic and antidepressant medication for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD003460. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003460.pub2. PMID 15846668.
- ^ Lesbros-Pantoflickova D, Michetti P, Fried M, Beglinger C, Blum A (2004). "Meta-analysis: The treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20 (11-12): 125369. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02267.x. PMID 15606387.
- ^ Jailwala J, Imperiale T, Kroenke K (2000). "Pharmacologic treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials.". Ann Intern Med 133 (2): 13647. PMID 10896640.
- ^ Talley N (2001). "Serotoninergic neuroenteric modulators.". Lancet 358 (9298): 20618. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)07103-3. PMID 11755632.
- ^ Joo J, Ehrenpreis E, Gonzalez L, Kaye M, Breno S, Wexner S, Zaitman D, Secrest K (1998). "Alterations in colonic anatomy induced by chronic stimulant laxatives: the cathartic colon revisited.". J Clin Gastroenterol 26 (4): 2836. doi:10.1097/00004836-199806000-00014. PMID 9649012.
- ^ Evans B, Clark W, Moore D, Whorwell P (2004). "Tegaserod for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD003960. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003960.pub2. PMID 14974049.
- ^ Tack J, Broekaert D, Fischler B, Oudenhove L, Gevers A, Janssens J (2006). "A controlled crossover study of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram in irritable bowel syndrome.". Gut 55 (8): 1095103. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.077503. PMID 16401691.
- ^ Vahedi H, Merat S, Rashidioon A, Ghoddoosi A, Malekzadeh R (2005). "The effect of fluoxetine in patients with pain and constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: a double-blind randomized-controlled study.". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 22 (5): 3815. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02566.x. PMID 16128675.
- ^ Creed F, Fernandes L, Guthrie E, Palmer S, Ratcliffe J, Read N, Rigby C, Thompson D, Tomenson B (2003). "The cost-effectiveness of psychotherapy and paroxetine for severe irritable bowel syndrome.". Gastroenterology 124 (2): 30317. doi:10.1053/gast.2003.50055. PMID 12557136.
- ^ Tabas G, Beaves M, Wang J, Friday P, Mardini H, Arnold G (2004). "Paroxetine to treat irritable bowel syndrome not responding to high-fiber diet: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.". Am J Gastroenterol 99 (5): 91420. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04127.x. PMID 15128360.
- ^ "UpToDate Inc.". http://www.uptodate.com/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=gi_dis/5811&selectedTitle=1~148&source=search_result#9.
- ^ Jackson J, O'Malley P, Tomkins G, Balden E, Santoro J, Kroenke K (2000). "Treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders with antidepressant medications: a meta-analysis.". Am J Med 108 (1): 6572. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(99)00299-5.
- ^ Drossman D, Toner B, Whitehead W, Diamant N, Dalton C, Duncan S, Emmott S, Proffitt V, Akman D, Frusciante K, Le T, Meyer K, Bradshaw B, Mikula K, Morris C, Blackman C, Hu Y, Jia H, Li J, Koch G, Bangdiwala S (2003). "Cognitive-behavioral therapy versus education and desipramine versus placebo for moderate to severe functional bowel disorders.". Gastroenterology 125 (1): 1931. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00669-3.
- ^ Sharara AI, Aoun E, Abdul-Baki H, Mounzer R, Sidani S, Elhajj I (2006). "A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of rifaximin in patients with abdominal bloating and flatulence". Am J Gastroenterol 101 (2): 32633. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00458.x.
- ^ Quigley EM (2006). "Germs, gas and the gut; the evolving role of the enteric flora in IBS". Am J Gastroenterol 101 (2): 3345. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00445.x.
- ^ Warfield, Carol A.; Zahid H. Bajwa (2003). Principles and Practice of Pain Medicine. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 0071443495.
- ^ Kennedy T, Jones R, Darnley S, Seed P, Wessely S, Chalder T (2005). "Cognitive behaviour therapy in addition to antispasmodic treatment for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial". BMJ 331 (7514): 435. doi:10.1136/bmj.38545.505764.06. PMID 16093252 Full text.
- ^ Heymann-M๖nnikes I, Arnold R, Florin I, Herda C, Melfsen S, M๖nnikes H (2000). "The combination of medical treatment plus multicomponent behavioral therapy is superior to medical treatment alone in the therapy of irritable bowel syndrome.". Am J Gastroenterol 95 (4): 98194. PMID 10763948.
- ^ van der Veek PP, van Rood YR, Masclee AA (2007). "Clinical trial: short- and long-term benefit of relaxation training for irritable bowel syndrome". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 26 (6): 94352. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03437.x (inactive 2009-05-07). PMID 17767479.
- ^ Nikfar S, Rahimi R, Rahimi F, Derakhshani S, Abdollahi M (December 2008). "Efficacy of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials". Dis. Colon Rectum 51 (12): 177580. doi:10.1007/s10350-008-9335-z. PMID 18465170.
- ^ Niedzielin K, Kordecki H, Birkenfeld B (2001). "A controlled, double-blind, randomized study on the efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum 299V in patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13 (10): 11437. doi:10.1097/00042737-200110000-00004. PMID 11711768.
- ^ "www.acg.gi.org" (PDF). http://www.acg.gi.org/media/releases/ACG05Release_ProbioticsinIBS.pdf.
- ^ Brenner DM, Moeller MJ, Chey WD, Schoenfeld PS (April 2009). "The utility of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 104 (4): 103349; quiz 1050. doi:10.1038/ajg.2009.25. PMID 19277023.
- ^ Madisch A, Holtmann G, Plein K, Holz J (2004). "Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with herbal preparations: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multi-centre trial". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19: 2719. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01859.x.
- ^ Hadley SK, Gaarder SM (2005). "Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome". Am Fam Physician 72 (12): 25016. PMID 16370407. http://www.aafp.org/afp/20051215/2501.html.
- ^ Nash P, Gould SR, Bernardo DE (1986). "Peppermint oil does not relieve the pain of irritable bowel syndrome". Br J Clin Pract 40 (7): 2923. PMID 3527248.
- ^ Liu JH, Chen GH, Yeh HZ, Huang CK, Poon SK (1997). "Enteric-coated peppermint-oil capsules in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective, randomized trial". J. Gastroenterol. 32 (6): 7658. doi:10.1007/BF02936952. PMID 9430014.
- ^ Lim B, Manheimer E, Lao L, Ziea E, Wisniewski J, Liu J, Berman B (2006). "Acupuncture for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD005111. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005111.pub2. PMID 17054239.
- ^ a b c Quigley EM, Locke GR, Mueller-Lissner S, Paulo LG, Tytgat GN, Helfrich I, Schaefer E. Prevalence and management of abdominal cramping and pain: a multinational survey. (2006 Jul). "Aliment Pharmacol Ther.". Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 24 (2): 4119. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02989.x. PMID 16842469.
- ^ Ehlin AG, Montgomery SM, Ekbom A, Pounder RE, Wakefield AJ. (2003 Aug). "Prevalence of gastrointestinal diseases in two British national birth cohorts.". Gut. 52 (8): 111721.. doi:10.1136/gut.52.8.1117. PMID 12865268.
- ^ Hungin AP, Chang L, Locke GR, Dennis EH, Barghout V (2005). "Irritable bowel syndrome in the United States: prevalence, symptom patterns and impact". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 21 (11): 136575. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02463.x. PMID 15932367.
- ^ Jafri W, Yakoob J, Jafri N Islam M, Ali QM. (2007). "Irritable bowel syndrome and health seeking behaviour in different communities of Pakistan.". J Pak Med Assoc. 57 (6): 2857. PMID 17629228.
- ^ Jafri W, Yakoob J, Jafri N, Islam M, Ali QM. (2005). "Frequency of irritable bowel syndrome in college students.". J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 4 (17): 911. PMID 16599025.
- ^ Tuteja AK, Talley NJ, Gelman SS, Adler SC, Thompson C, Tolman K, Hale DC. E. (2007). "Development of Functional Diarrhea, Constipation, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and Dyspepsia During and After Traveling Outside the USA.". Dig. Dis. Sci 53: 271. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9853-x. PMID 17549631.
- ^ Leong SA, Barghout V, Birnbaum HG, et al. (2003). "The economic consequences of irritable bowel syndrome: a US employer perspective". Arch. Intern. Med. 163 (8): 92935. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.8.929. PMID 12719202.
- ^ Martin B, Ganguly R, Pannicker S, Feride F, Barghout V (2003). "Utilization Patterns and Net Direct Medical Costs Medicaid of Irritable Bowel Syndrome". Curr Med Res Opin 19 (8): 77180. doi:10.1185/030079903125002540. PMID 12719202. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/465472.
- ^ Brown PW (1950). "The irritable bowel syndrome". Rocky Mountain medical journal 47 (5): 3436. PMID 15418074.
[edit] External links
- UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders
- Irritable bowel syndrome at the Open Directory Project
IBS.HTM